What is Genesis Block? 🫡
We take a deeper look at the fundamental concept in crypto, the foundation upon which all subsequent blocks are built on a blockchain.
Hello, y'all. If you think you know your music, then this is for you frens. A complete go. Check out 👉 Asset - Music Nerd
This is The Token Dispatch 🙌 you can hit us on telegram 🤟
The genesis block is a fundamental concept in crypto.
Understanding the Significance
It refers to the first block in a blockchain, and contains unique characteristics that distinguish it from other blocks.
Establishes the original state of the network, sets parameters for future blocks, and provides a fixed starting point for the blockchain.
The foundation upon which all subsequent blocks are built.
It contains crucial information about the creation of the blockchain, including its initial parameters and configurations.
This data sets the stage for how transactions will be processed, verified, and recorded moving forward.
Creation Process and Contents
When creating a new blockchain, developers must manually define the contents of the genesis block.
This includes details like the timestamp, difficulty target (for proof-of-work systems), and any initial transactions or "coins" that need to be distributed among participants.
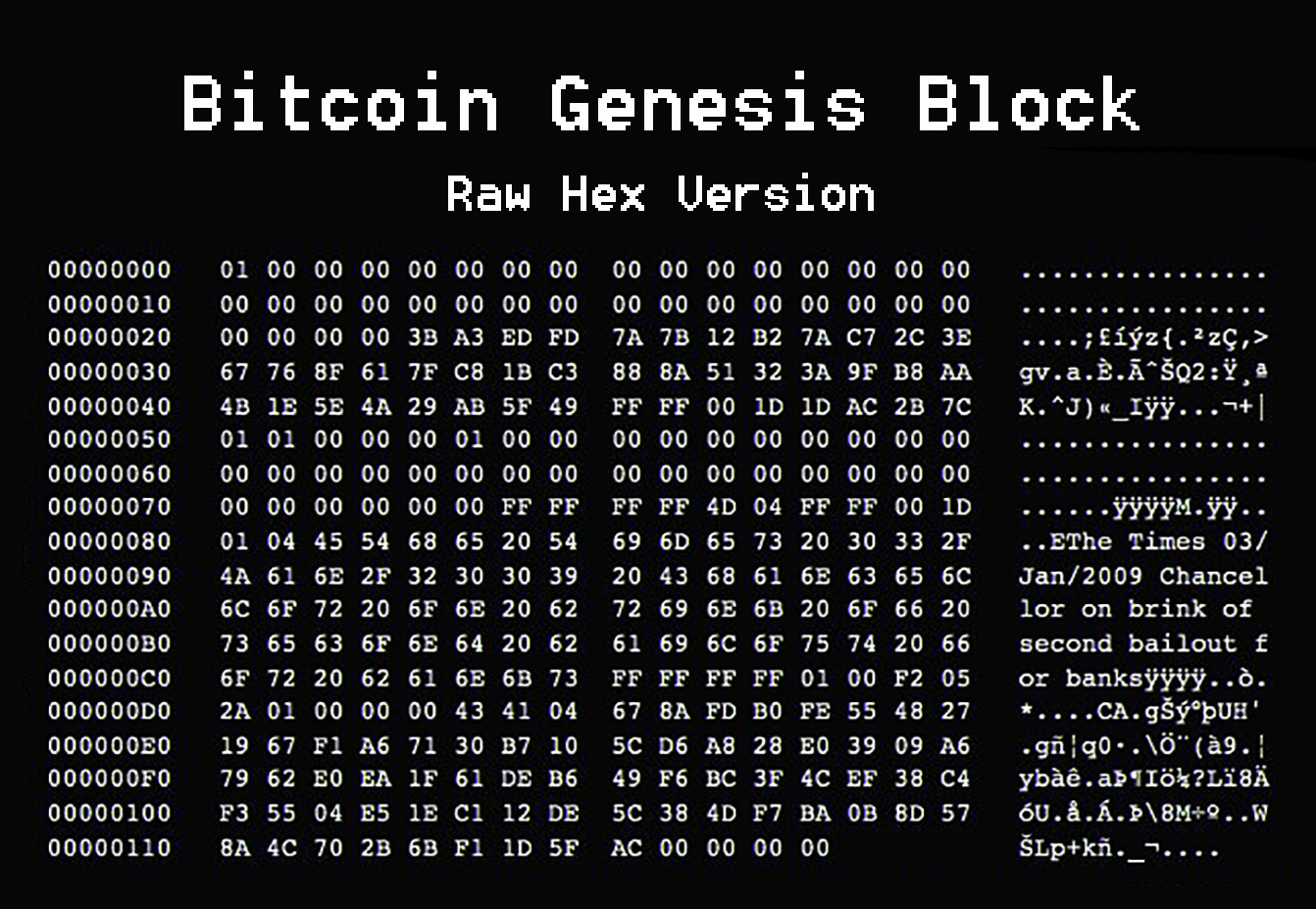
For example: Satoshi Nakamoto, the pseudonymous creator of Bitcoin, included a headline from The Times newspaper in the genesis block as a way to signal the urgency behind developing a decentralised digital currency.
Examples in Popular Cryptocurrencies
Bitcoin (BTC): Genesis block was created by Satoshi Nakamoto on January 3rd, 2009, at approximately 6:15 PM UTC. It contained 50 Bitcoins—the reward for solving the very first block—which were sent to the address 1A1zP1eP5QGefi2DMPTfTL5SLmv7DivfNa.
Ethereum (ETH): Vitalik Buterin, co-founder of Ethereum, launched the platform's genesis block on July 30th, 2015. Unlike Bitcoin, Ethereum does not have a fixed total supply; instead, new Ether tokens are minted through a process called mining. At launch, there were already around 72 million pre-mined Ether coins in circulation due to Ethereum's crowd sale event held prior to its official release.
Litecoin (LTC): Litecoin, created by Charlie Lee, mined its genesis block on October 7, 2011. This block laid the groundwork for the Litecoin blockchain and introduced the Scrypt hashing algorithm, aiming to provide faster block creation times compared to Bitcoin.
Implications for Miners and Users
For miners, understanding the specifications of the genesis block can help them optimise their mining operations by adjusting settings accordingly. Users should take note of the rules established within the genesis block since they dictate various aspects of the blockchain, such as transaction fees and maximum supply limits.
Significance in Blockchain
Foundation of Blockchain: The beginning of the entire chain of blocks. The initial state of the network, sets parameters for subsequent blocks, and the basis for the decentralised ledger system for cryptocurrencies.
Immutability and Trust: Transparent and immutable ledger system by preventing retroactive alterations, maintaining the integrity of the entire blockchain. Provide historical record of all transactions on the network.
Symbolic and Philosophical Message: The Genesis Block often contains a message from the creator(s) of the blockchain, reflecting the ethos and vision behind the cryptocurrency movement.
For example: The Bitcoin Genesis Block included a timestamp and a cryptic message from Satoshi Nakamoto, commenting on the need for a decentralised currency and critiquing the traditional financial system. This message adds a symbolic and philosophical layer to the Genesis Block, emphasising its significance beyond its technical role.
Security and Consensus: All participants start with the same starting point and agree on the validity of subsequent blocks through consensus. Any attempt to modify or tamper with the Genesis Block would invalidate the entire chain, making the blockchain resistant to manipulation and ensuring the transparency and security of transactions.
Influence on Development
Establishing Initial Supply and Scarcity: Set the initial supply of bitcoins at 50, which halved every 210,000 blocks, leading to a fixed limit of 21 million bitcoins. This scarcity has made Bitcoin an attractive store of value, influencing its price appreciation and creating a digital asset with limited availability.
Introducing Proof-of-Work Algorithm: A fundamental component of blockchain security and decentralisation. This algorithm requires miners to solve complex mathematical problems to validate transactions, ensuring network security and preventing centralisation.
Embodying Decentralisation Ethos: By creating a peer-to-peer financial system that challenges traditional financial institutions and governments. Inspiring a movement towards decentralised finance and transparent transactions.
Pioneering Technological Advancements: By introducing blockchain technology that revolutionised trust, transparency, and decentralisation. It inspired the creation of a new era of technological innovation with the potential to transform various industries.
Cultural Significance and Inspiration: Extends beyond Bitcoin's creation, inspiring the development of numerous other cryptocurrencies and blockchain-based applications. It has become a symbol of innovation, financial revolution, and decentralised peer-to-peer finance.
Criticisms of the genesis block
Symbolic Message Interpretation: The inclusion of a message in the Genesis Block, such as the one in Bitcoin's Genesis Block referencing a financial crisis headline, has been subject to interpretation and criticism. Some view these messages as potentially controversial or politically charged, leading to debates about the intended meaning and impact of such messages on the cryptocurrency ecosystem.
Immutability Challenges: While the immutability of the Genesis Block is a core feature of blockchain technology, it has also faced criticism for its rigidity. Once the Genesis Block is established, it cannot be altered, potentially leading to situations where outdated or problematic information is permanently embedded in the blockchain, raising concerns about historical accuracy and relevance over time.
Decentralisation Concerns: The centralised creation of the Genesis Block, often by a single entity or a small group of individuals, has raised concerns about the initial distribution of power and influence within the cryptocurrency network. Critics argue that this centralised genesis could contradict the principles of decentralisation that cryptocurrencies aim to uphold, leading to issues of control and governance in the network.
Economic and Social Implications: The significance of the Genesis Block in establishing the initial supply of tokens and setting the tone for the cryptocurrency's economic model has been a point of contention. Critics question the fairness of initial token distribution, the impact on wealth distribution, and the long-term economic implications of decisions made in the Genesis Block, highlighting concerns about inequality and economic sustainability within cryptocurrency networks.
The complex interplay between the symbolic, technical, economic, and social dimensions of the Genesis Block present challenges within the crypto ecosystem.
TTD Week That Was 📆
Saturday: Where Goes Ethereum? 🚩
Friday: Crypto Hunger Games 🧟♀️
Thursday: Are We Consolidating? 🤷♀️
Wednesday: Fear The Fed 😰
Tuesday: Brakes On. Still Strong 🏋️♂️
Monday: Solana ❤️
TTD Week in Funding 💰
Espresso Systems. $28 million. An EVM-compatible blockchain that provides scaling and privacy systems for Web 3 applications.
Succinct. $43 million. Decentralised prover network to build blockchain applications and infrastructure secured by cryptographic truth, not trust.
Rails. $6.2 million. A self-custodial crypto exchange that leverages a centralised order book to drive optimal trade execution
If you like us, if you don't like us .. either ways do tell us✌️
If you dig what we do, show us love on Twitter, Instagram & Threads🤞
So long. OKAY? ✋